Dummy Post: To Quantify or Not to Quantify, That Is the Question
Our chromatography team is regularly asked to identify compounds in materials. Some projects only require the identification of compounds, while others require the accurate determination of concentration of the identified compounds. The latter, termed quantitative chromatography, requires the preparation of calibration standards suitable for the compound in question. At a recent dinner, one of our […]
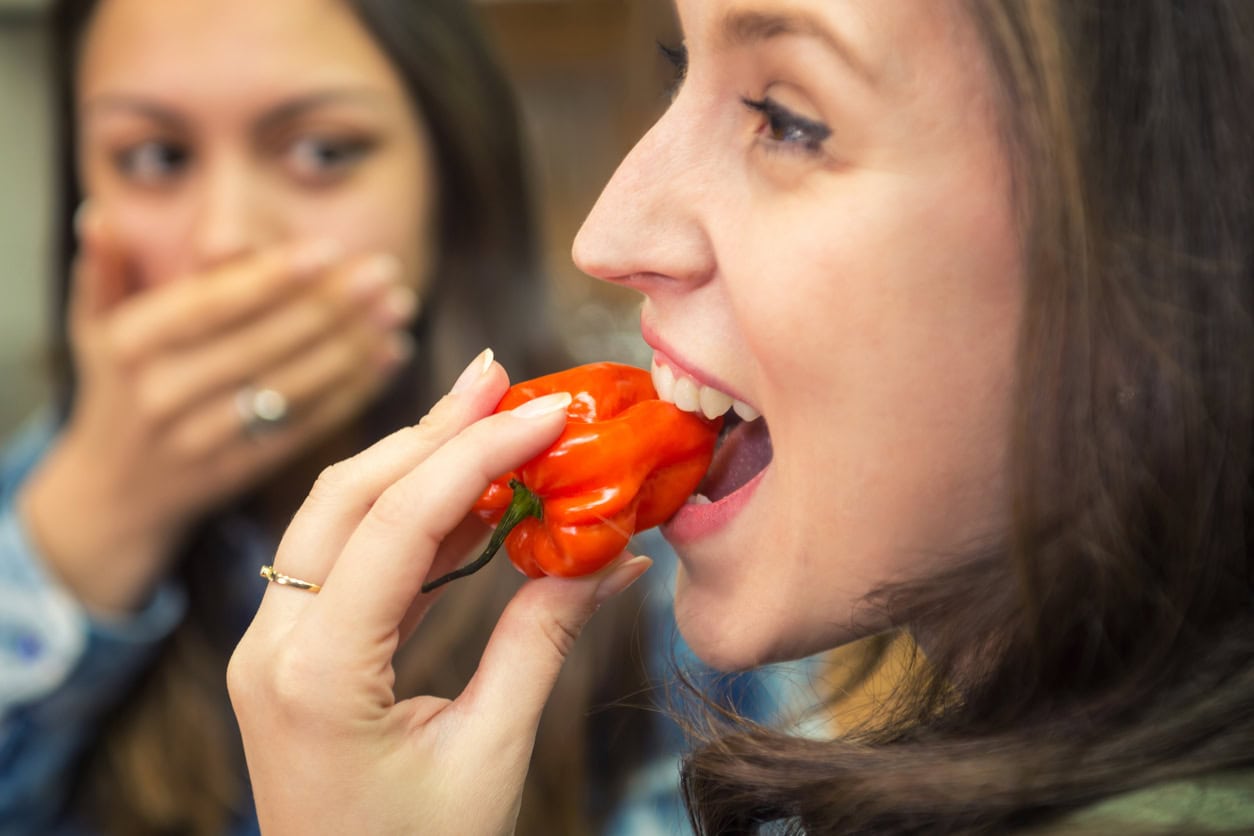

Caliente Chromatography: Quantitative Analysis of Capsaicin
Chromatography: To Quantify or Not to Quantify, That Is the Question Our chromatography team is regularly asked to identify compounds in materials. Some projects only require the identification of compounds, while others require the accurate determination of concentration of the identified compounds. The latter, termed quantitative chromatography, requires the preparation of calibration standards suitable for […]
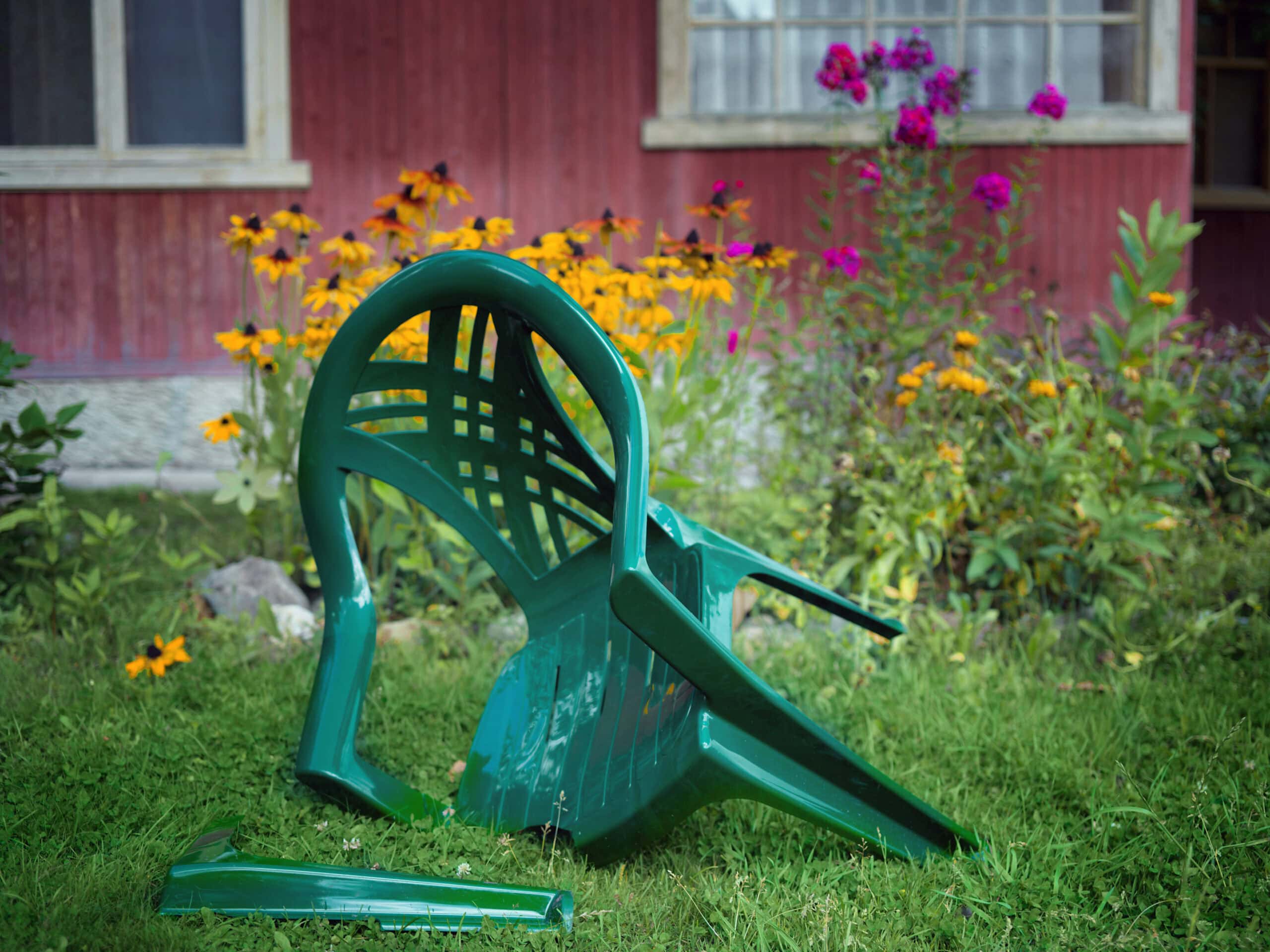 Abandoned plastic garden chair with broken leg, outdoor shot
Abandoned plastic garden chair with broken leg, outdoor shot
How Long Can a Polymer Last…And What Is Q10?
The longevity of polymers in real-world use is a critical importance across industries, from medical devices and packaging to consumer products and infrastructure. While many polymers are engineered to withstand sunlight, heat, moisture, and chemical exposure, nearly everyone has seen a once-flexible product turn brittle, discolored, or cracked over time. Both raw materials (such as […]
I Have a Little Robot
I have a little robot, For minimally invasive care, With polymer housings, cable sheaths, And coatings tuned for wear. It moves by catheter guidance, With robotic hands outside, The console shapes its pathway While surgeons steer inside. A handheld little robot Helps line the cuts just right, It tracks the plan from CT scans For guided […]

2026: The Year Ahead from Cambridge Polymer Group
In 2026, robotics and AI will continue to receive substantial attention across all industries, including medical devices. The expanding adoption of robotics and AI will coincide with other significant pressures that will impact medical devices. These include the recent 10993-1 update, and how the FDA views this update, as well as ongoing tariff and onshoring […]
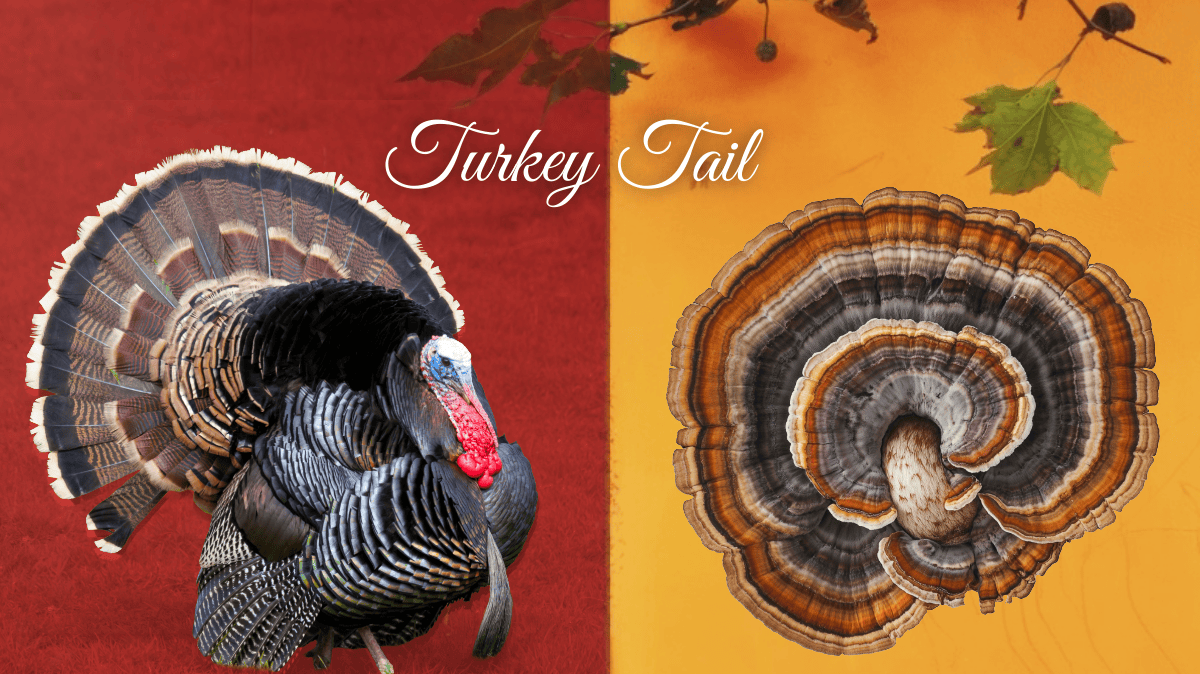

From Forest Floor to Food Wrap: Turkey Tail Mycelium at the Frontiers of Polymer Science
By early December, most Thanksgiving turkeys have migrated to stock pots and storage containers, but in forests across New England and beyond, turkey tail (Trametes versicolor) spreads over fallen logs in familiar bands of brown and cream. It draws attention less for its resemblance to the holiday bird than for its polymer-rich tissues that enable […]
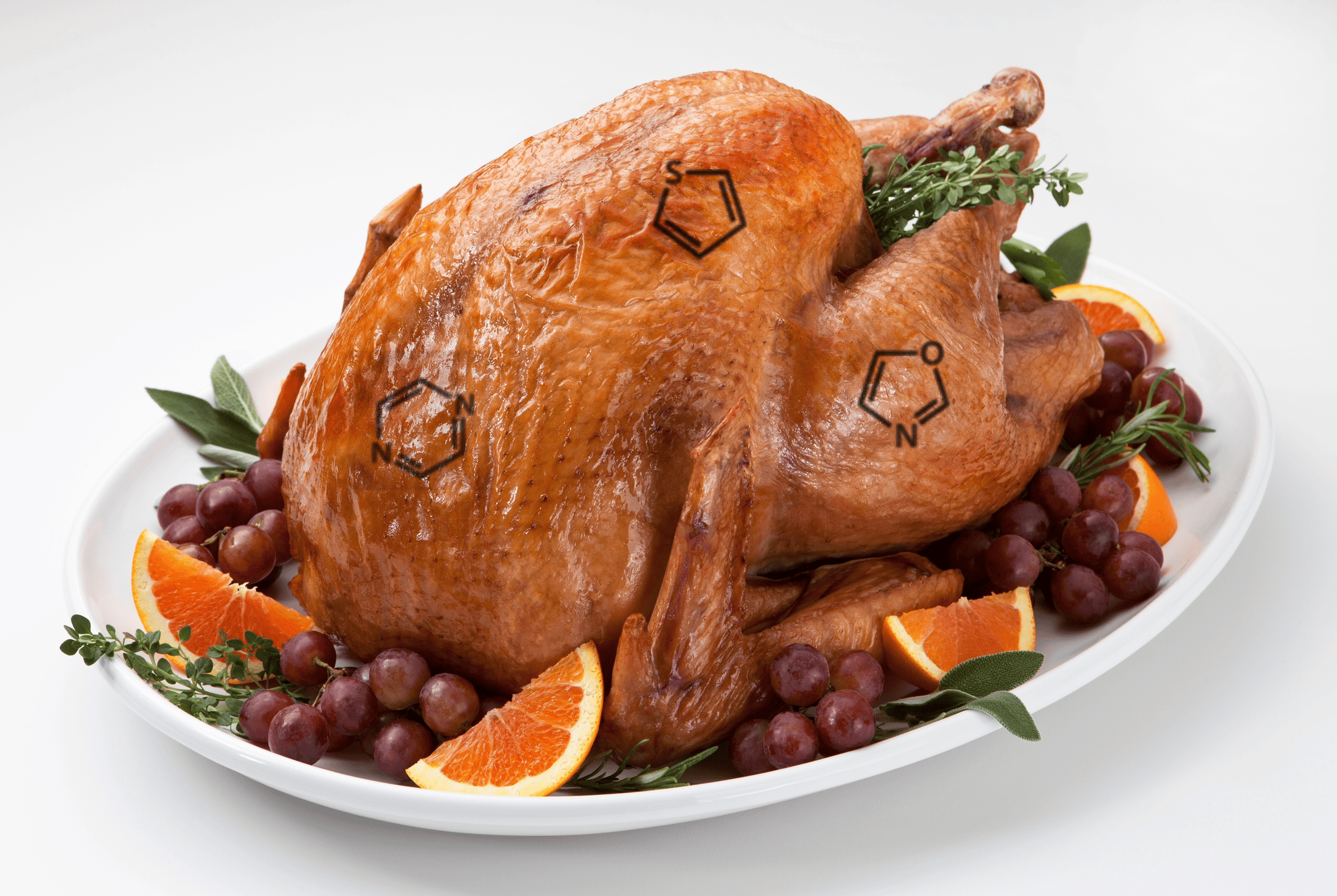
The Chemistry Behind the Perfect Roast: Understanding the Maillard Reaction
Every time you roast a turkey or bake bread, a fascinating chemical reaction gives your food its rich brown color, enticing aroma, and complex flavors. That reaction is called the Maillard reaction (pronounced my-ard), a cornerstone of both food chemistry and polymer science. What Is the Maillard Reaction? The Maillard reaction occurs when amino acids […]
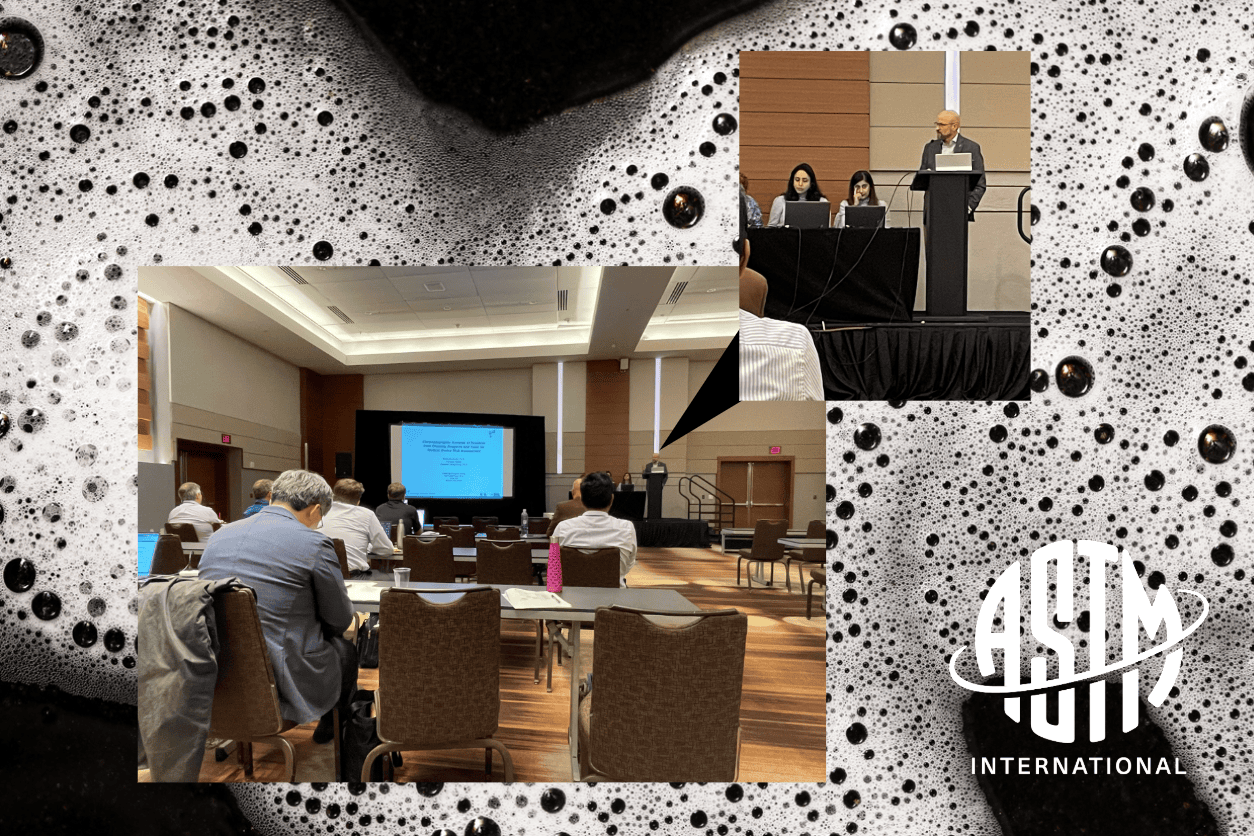

ASTM F04.15.17 Workshop Highlights Advancing Standardization in Medical Device Cleaning
The ASTM Committee F04.15.17 on Medical Device Cleaning recently held a workshop focused on the analysis of cleaning agents used for both new and reusable medical devices. The goal was to identify key topic areas requiring standardization to help ensure the development of safe, effective, and well-characterized products across the medical device industry. The morning […]

Why Getting Material Selection Right Matters in Medical Device Design Live Event
Selecting the right material from day one can make or break a modern medical device. Join Cambridge Polymer Group for “Getting Material Selection Right the First Time” with industry leader Dr. Gavin Braithwaite on November 12, 2025, at 2:00pm EST. Register Here Why Early Material Choices Matter Medical device development today is a balancing act. […]

Bridging the Gap in Material Science Expertise: Explore the New Campoly.com
We are excited to unveil the new campoly.com, the redesigned digital home for Cambridge Polymer Group, Inc. (“CPG”)! This launch marks a major milestone in our commitment to providing advanced contract testing, research, and development services in material science for clients across all industries, with particular emphasis on healthcare. Why We Redesigned Over the past […]
