
Call for Abstracts: ASTM Workshop on Reprocessing of Re-usable Medical Devices
A Workshop on Reprocessing of Re-usable Medical Devices will be held Tuesday, November 15, 2016. Sponsored by ASTM Committee F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and, the workshop will be held at the Renaissance Orlando at SeaWorld in Orlando, FL, in conjunction with the November standards development meetings of the committee. Objectives: A recent article […]

Biomed Device Exposition in Boston
Cambridge Polymer Group will be exhibiting at the Biomed Device Exposition in Boston on May 6-7th. Come visit us at booth 1147 to see the new analytical tools, formulation capabilities, and project assistance we can provide. If you would like to visit our lab while you are in town, please contact us at info@campoly.com. Details […]
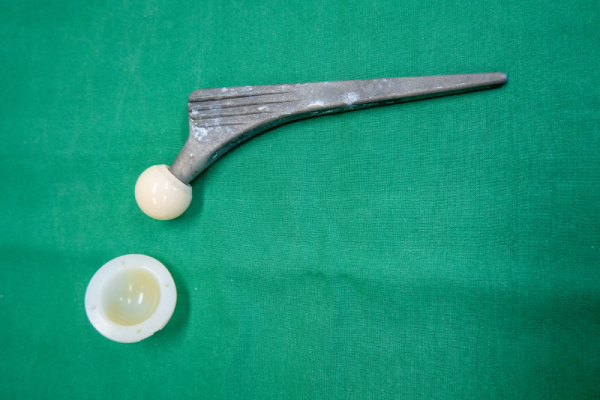
Molecular Weight Characterization to Assess Aging in Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene
Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is commonly used as a bearing surface in hip, knee, shoulder, and other total joint replacement arthroplasties. Aging of UHMWPE that has been irradiated without additional treatment to stabilize the residual free radicals can result in oxidation followed by chain scissioning. Researchers will usually measure oxidation index to characterize […]

Choc Full of Information
Chocolate is a complex structure containing consisting of cocoa powder, sugar, fat solids (primarily cocoa butter). The cocoa powder and cocoa butter both come from the cocoa bean following roasting, grinding, and liquification. The flavor and mouth feel of chocolate will depend on the ratios of these components, as well as their size and structure. […]

Bubble Point for Pore Size Measurements
The pore size in filters, membranes, and fabrics can be determined at Cambridge Polymer Group by a variety of methods, including optical and scanning electron microscopy, mercury porosimetry, and particle size exclusion. A commonly used method is ASTM F316 “Pore size characteristics of membrane filters by bubble point and mean flow pore test.” This standard […]

MIT Polymer Symposium
CPG was a sponsor of MIT’s 5th annual Polymer Day Symposium, held on March 11, 2015 at MIT. The event is hosted by MIT’s Program in Polymers and Soft Matter. A poster session was held in the morning, and two CPG scientists, Svirkin and Kozak, acted as judges, and awarded prizes to the top posters. […]

How To Determine If Your Medical Devices Are Clean
The success of a medical device depends on both the details of its design and the proper selection of materials from which it is fabricated, taking in to account its final use and regulatory requirements. Success also depends on how it is manufactured, and a critical feature of medical device manufacturing is ensuring a suitably […]

Using Free Radicals To Monitor Engine Oil Age
Car owners are advised to change their engine oil every 3000-5000 miles. But what is actually happening to the oil over time in the engine? We have heard about the benefits of antioxidants in the body. Antioxidants also help engine oil. In use, engine oil is subjected to high temperatures and high shear stresses which […]
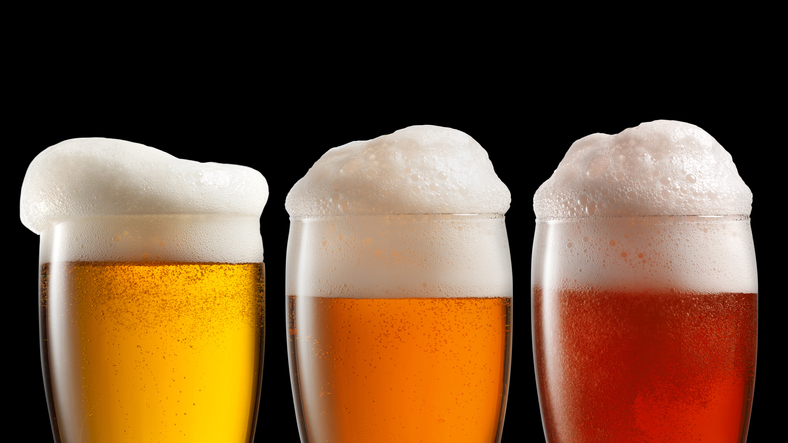

The Rheology of Beer
Princeton scientists Alban Sauret, Francois Boulonge, Emilie Dressaire, and Howard Stone have applied fluid dynamics and rheology to help long-suffering beer drinkers understand why beer with a head of foam are less likely to slosh and spill compared to their counterparts with less foam. Simple experiments, like the images shown above, indicate that reducing the […]
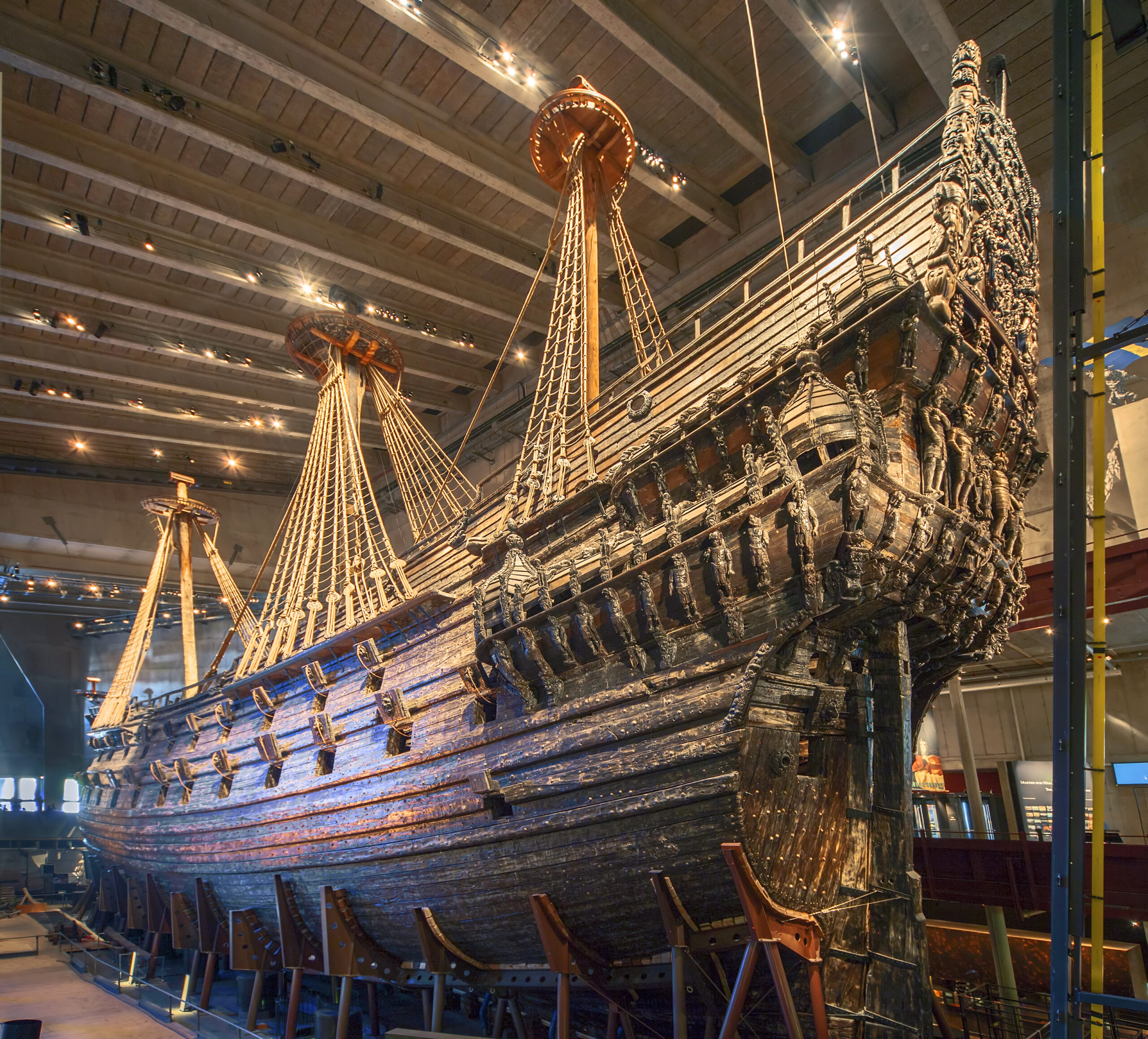

Swedish Warships and Quality Management Systems
In the design of a new device, a good manufacturer will follow quality management principles to ensure the device meets the requirements of the end-user. What does this have to do with Swedish warships? History can provide us with useful lessons on quality management systems. The Vasa was a warship built in 1626 that holds […]
