ASTM F640 – Standard Test Methods for Determining Radiopacity for Medical Use
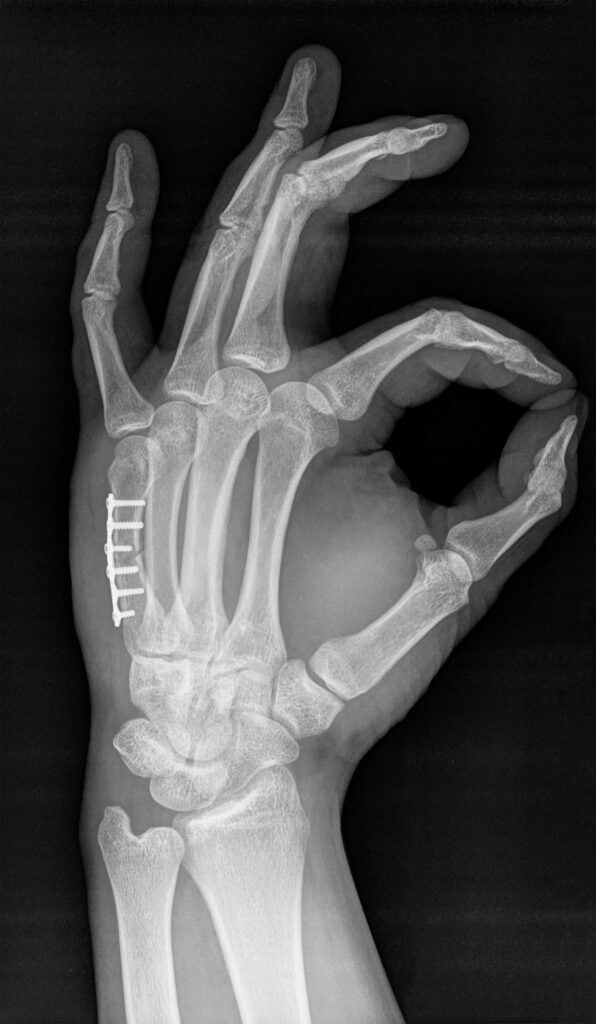
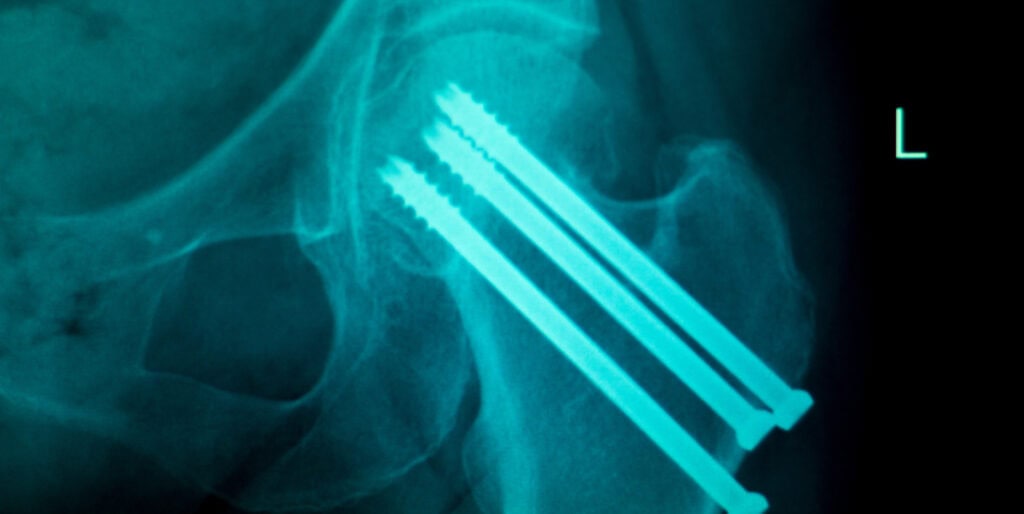
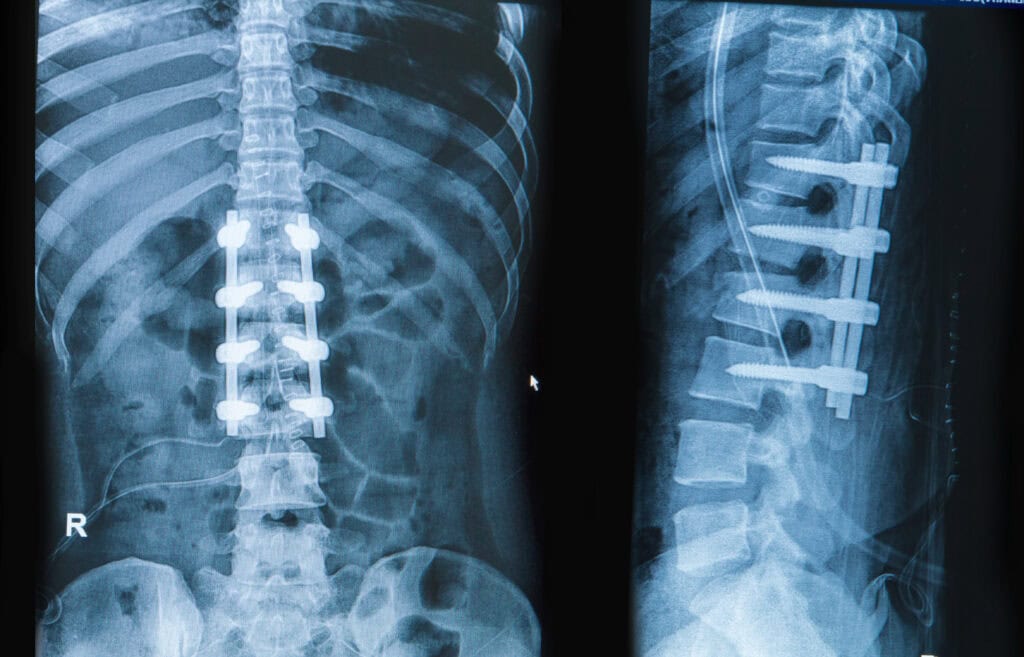
Radiopacity is the ability of a material or object to block, or attenuate, x-rays. Variables such as elemental composition, density, and dimensions (relative to the x-ray beam path) all affect radiopacity. In the biomedical and associated fields, determining radiopacity is vital to demonstrate the ability to track an implantable device or surgical tool in vivo using x-ray, fluoroscopy, or computed tomography (CT). Equally, surfaces such as operating room tables or patient positioning mats that support patients during imaging must also be characterized. Although the former are largely covered by tests such as ASTM F640, the latter are defined in the Federal Regulations within the US (21CFR part 1020). Cambridge Polymer Group performs radiopacity testing that is compliant with these standards.
Why is Radiopacity Important?
- Localization: Radiopacity helps in locating the device within the body during surgical procedures, making it easier to retrieve or manipulate.
- Assessment of Device Position: It allows for the assessment of the device’s position and orientation after implantation, ensuring proper placement and function.
- Detection of Complications: Radiopacity can help detect potential complications such as device migration.
- Treatment Planning: Imaging studies with visible medical devices aid in planning subsequent medical interventions.
Radiopacity Testing Procedure
- Sample Preparation: The medical device is prepared according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Reference Standard: Typically, a standardized aluminum step wedge is used as a reference for comparison. The step wedge has varying thicknesses of aluminum, each representing a different level of radiopacity. Alternatively, a predicate device may be tested for comparison.
- Radiographic Exposure: The device and the reference standard are placed side-by-side and exposed to X-rays.
- Image Analysis: The resulting x-ray image is analyzed to determine the contrast between the device and the background. In digital x-ray imaging, contrast is calculated as a pixel intensity (greyscale) difference.
- Radiopacity Level: The pixel intensity difference determined for the device is compared to the pixel intensity difference of the reference standard. If using an aluminum step wedge, the radiopacity of the device is then expressed in terms of the equivalent thickness of aluminum. If a predicate device or alternative standard is used, comparison of the pixel intensity differences can be made to indicate if the device is more or less radiopaque than the standard.
Contact our experts today for a quote for radiopacity testing of your device.